1. 简介
github仓库地址:https://github.com/uber-go/ratelimit
文档地址:https://pkg.go.dev/go.uber.org/ratelimit
ratelimit 是一个 Go 语言实现的基于漏桶算法的限流库,它的实现根据不同请求之间的时间差来填充漏桶,而不是用一个固定频率的时钟来填充。
系统为了防止瞬时流量过大,所造成的本服务、数据库、第三方服务接口请求的压力过大,通常需要对请求进行限流。
2. 使用
以下示例引用自官方仓库的 README 文件的使用示例。
ratelimit 的使用非常简单,先创建一个 ratelimit 对象,指定每秒的频率限制(RPS),然后通过 Take 方法来获取频控,程序将会阻塞直至得到当前一次频控。
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"go.uber.org/ratelimit"
)
func main() {
rl := ratelimit.New(100) // 创建一个 ratelimit 对象,指定每秒的频率限制
prev := time.Now()
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
now := rl.Take() // 获取频控
fmt.Println(i, now.Sub(prev))
prev = now
}
}
New 函数创建的限流器默认是每秒的频率限制,通过配置参数可以改变时间间隔。
rl := ratelimit.New(100) // 创建一个每秒100次限制的限流器
rl := ratelimit.New(10, ratelimit.Per(time.Minute)) // 创建一个每分钟10次限制的限流器
3. 开发文档
3.1 类型
Limiter 是限流器接口,用来对某种过程进行频率控制,支持跨协程间的控制。程序需要通过调用 Take 方法来获取频控,获取不到时将会阻塞等待。
type Limiter interface {
// Take should block to make sure that the RPS is met.
Take() time.Time
}
Option 是限流器的配置参数。
type Option interface {
// contains filtered or unexported methods
}
// WithoutSlack 让限流器无松弛量
var WithoutSlack Option = slackOption(0)
Clock 是创建一个带有时钟的限流器的最简化接口。
type Clock interface {
Now() time.Time
Sleep(time.Duration)
}
3.2 函数
// New 创建指定每秒频控的限流器
func New(rate int, opts ...Option) Limiter
// NewUnlimited 创建无限频控的限流器
func NewUnlimited() Limiter
// Per 指定时间间隔的选项,默认时间间隔是秒,可以指定为分钟等其他时间间隔
func Per(per time.Duration) Option
// WithClock 指定时钟的选项,替换默认的定时时钟,通常用来mock做测试
func WithClock(clock Clock) Option
// WithSlack 指定松弛量的选项
func WithSlack(slack int) Option
4. 源码分析
4.1 最大松弛量
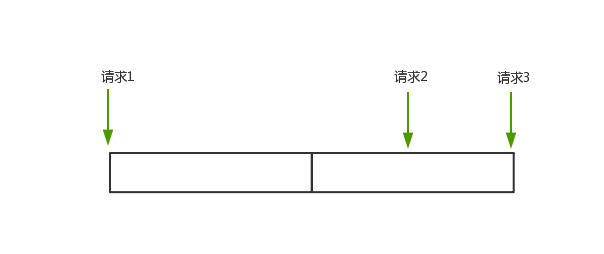
传统的漏桶算法对于每个请求的时间间隔是固定的。例如一个 100 次每秒的限流器,每次请求的时间间隔为 10ms,当一个请求到来后,要至少等待 10ms 之后才能处理下一个请求。如果其中两个请求之间间隔大于 10ms,那这一秒限流器支持的请求限制就必然会小于 100 次。
而在实际使用中,流量经常是突发性的,是时间间隔不稳定的。例如第一次请求 15ms 后产生第二次请求,然后 5ms 后产生第三次请求,第三次请求就因为和第二次请求不足 10ms 而需要等待 5ms,三个请求需要消耗 25ms。
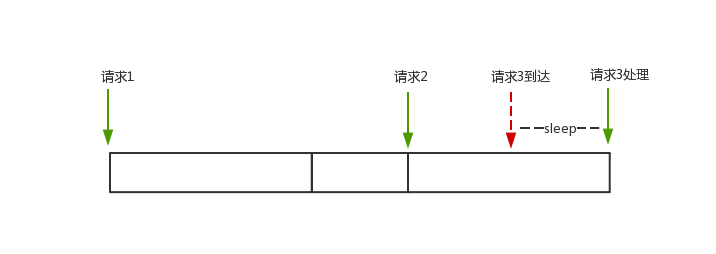
ratelimit 对漏桶算法做了一些改良,引入了最大松弛量(maxSlack)的概念。对于以上的例子,因为从请求一到请求二多等了 5ms,可以把这 5ms 挪给请求三使用,因而请求三无需等待,直接处理。三个请求只需要消耗 20ms。
但是如果两次请求之间时间间隔过久,比如高出平均时间间隔一两个数量级,那后面多个请求到来时,这个松弛量会被立刻消耗完,这里也就失去了限流的意义。为了防止这种情况,ratelimit 引入最大松弛量(maxSlack),表示允许抵消的最长时间。
maxSlack 等于平均时间间隔乘以松弛量 slack,slack 的默认值是 10,可以在创建限流器时指定设置,或者设置为 0 表示不用松弛量。
// 平均时间间隔 = 统计时间 / 频次
perRequest = config.per / time.Duration(rate)
// 最大松弛量 = slack * 平均时间间隔
maxSlack = time.Duration(config.slack) * perRequest
4.2 选项
ratelimit 的选项有 3 种,定义在结构体 config 的三个成员变量中。
// config configures a limiter.
type config struct {
clock Clock
slack int
per time.Duration
}
配置选项 Option 是一个接口类型,只要实现了 apply 方法就相当于实现了 Option 接口,也就是将设置写入结构体 config 中。clockOption、slackOption、perOption 三个类型都实现了 apply 方法,分别将三种选项写入结构体 config 中。
// Option configures a Limiter.
type Option interface {
apply(*config)
}
type clockOption struct {
clock Clock
}
func (o clockOption) apply(c *config) {
c.clock = o.clock
}
type slackOption int
func (o slackOption) apply(c *config) {
c.slack = int(o)
}
type perOption time.Duration
func (p perOption) apply(c *config) {
c.per = time.Duration(p)
}
在应用配置选项的函数 buildConfig 中就是针对 Option 切片依次执行 apply 方法。该函数由 New 函数调用,调用处就可以很灵活地传 0 到多个选项。
// buildConfig combines defaults with options.
func buildConfig(opts []Option) config {
c := config{
clock: clock.New(),
slack: 10,
per: time.Second,
}
for _, opt := range opts {
opt.apply(&c)
}
return c
}
4.3 创建
Limiter 是限流器接口,结构体 atomicInt64Limiter 实现了该接口。
type Limiter interface {
Take() time.Time
}
type atomicInt64Limiter struct {
prepadding [64]byte // 避免伪共享
state int64 // 下个允许频控获取的纳秒时间戳,初始化为0
postpadding [56]byte // 避免伪共享,减掉了 state 字段的 8 字节
perRequest time.Duration // 平均时间间隔
maxSlack time.Duration // 最大松弛量
clock Clock
}
New 函数创建一个新的限流器。默认统计时间为秒,创建参数 rate 表示频次,创建一个 rate 次每秒的限流器。也可以通过配置选项设置成分钟或其他,创建一个分钟级或其他时间级的限流器。
// New returns a Limiter that will limit to the given RPS.
func New(rate int, opts ...Option) Limiter {
return newAtomicInt64Based(rate, opts...)
}
// newAtomicBased returns a new atomic based limiter.
func newAtomicInt64Based(rate int, opts ...Option) *atomicInt64Limiter {
config := buildConfig(opts) // 应用配置选项
perRequest := config.per / time.Duration(rate) // 平均时间间隔 = 统计时间 / 频次
l := &atomicInt64Limiter{ // 初始化 atomicInt64Limiter 对象
perRequest: perRequest,
maxSlack: time.Duration(config.slack) * perRequest, // 最大松弛量
clock: config.clock,
}
atomic.StoreInt64(&l.state, 0)
return l
}
4.4 获取频控
程序使用 Take 方法获取频控。
func (t *atomicInt64Limiter) Take() time.Time {
var (
newTimeOfNextPermissionIssue int64 // 下次频控获取的纳秒时间戳
now int64
)
for {
now = t.clock.Now().UnixNano() // 当前时间的纳秒时间戳
timeOfNextPermissionIssue := atomic.LoadInt64(&t.state) // 限流器记录的允许频控获取的纳秒时间戳
switch { // 设置下次频控获取的纳秒时间戳
case timeOfNextPermissionIssue == 0 || (t.maxSlack == 0 && now-timeOfNextPermissionIssue > int64(t.perRequest)):
// 第一次获取频控 or 最大松弛量为0且现在比允许频控获取的时间超出一次间隔,现在可以获取频控
newTimeOfNextPermissionIssue = now
case t.maxSlack > 0 && now-timeOfNextPermissionIssue > int64(t.maxSlack):
// 现在比允许频控获取的时间超出最大松弛量,减去最大松弛量
newTimeOfNextPermissionIssue = now - int64(t.maxSlack)
default:
// 上次频控获取加上平均时间间隔
newTimeOfNextPermissionIssue = timeOfNextPermissionIssue + int64(t.perRequest)
}
// 当取出 state 的值与当前 state 的值相等,证明 state 没有被其他协程修改
// 获取当前调用的下次频控获取的纳秒时间戳,并设置 state,退出循环
if atomic.CompareAndSwapInt64(&t.state, timeOfNextPermissionIssue, newTimeOfNextPermissionIssue) {
break
}
}
sleepDuration := time.Duration(newTimeOfNextPermissionIssue - now)
if sleepDuration > 0 { // 休眠直到下次频控获取时间,返回该时间
t.clock.Sleep(sleepDuration)
return time.Unix(0, newTimeOfNextPermissionIssue)
}
// 无需休眠,直接返回当前时间
return time.Unix(0, now)
}